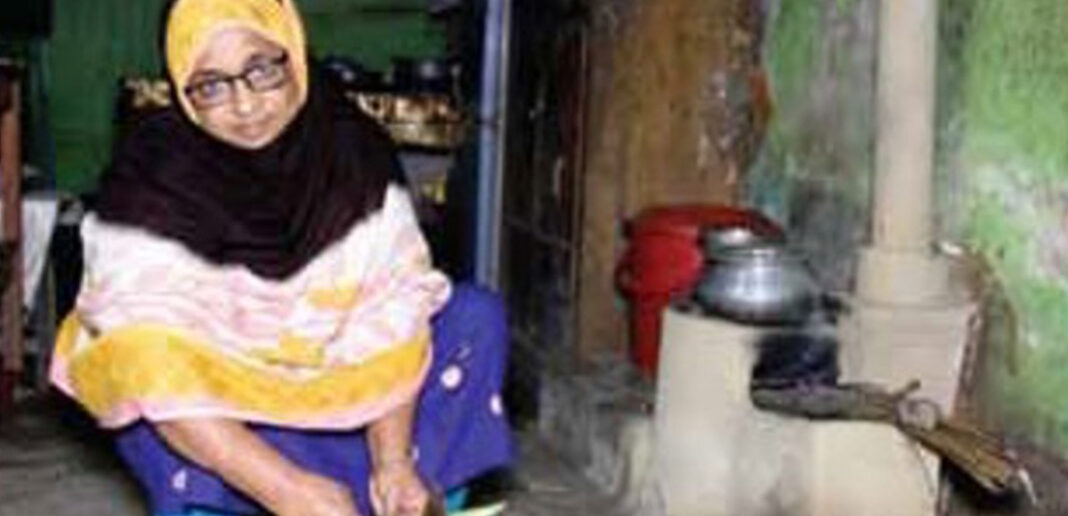
The traditional cooking practice in Bangladesh uses a “three-stone” cooking stove. Only 5%-10% of the house holds in Bangladesh use fossil fuels such as kerosene or liquated petroleum gas for cooking. The majority uses a mix of agricultural residues, twigs, leaves, cow dung, and firewood. The combustion of some of this biomass in the traditional cooking stoves generates a variety of gases including carbon dioxide (CO2), carbon monoxide, and other particulate matters. The replacement of traditional stoves by improved cooking stoves (ICS) improves heat transfer, which reduces the total amount of fuel required for cooking and the amount of emissions. Altogether, the improved cook stoves have the following benefits-
• Yearly reduction of Carbon Di-oxide emission is 2.145 tons per ICS
• Yearly savings of fuel wood 1.277 tons per stove
• Fuel and time consumption of ICS is 50% less than those of traditional stoves.
• Saves money
• Almost smoke-free environment that ensures healthy life, especially of mother and children.
Goal
Energy Efficiency
Geographical Coverage
Chakaria, Moheshkhali, Pekua, Ramu, Cox’s Bazar Sadar & Ukhiya Upazilas of Cox’s Bazar District; Banshkhali & Lohagora Upazilas of Chottogram district; Lama upazila of Bandarban District and Kapasia Upazila of Gazipur District.
Objective
• To save traditional fuels by the popularization of the improved stove and keep pollution free environment in rural areas
• To reduce indoor air pollution (IAP) in the kitchen.
• To develop skilled manpower through the training course of improved stoves to the unemployed men and women of the country
• To create awareness about the effectiveness and usefulness of improved stoves by massive advertisements through various media.
• To reduce deforestation and maintain the ecological balance of the country by the massive use of the improved stove.
• To involve different Government, Semi-Government and Non-Government Organizations in the dissemination program of improved stoves.
• To improve the hygienic condition of the kitchen
Major Activities
• Training on benefits ICS.
• Courtyard meeting on climate change and impact of deforestation.
• Session on Health hazards due to indoor smoke.
• Awareness raising session on air pollution.
Achievements
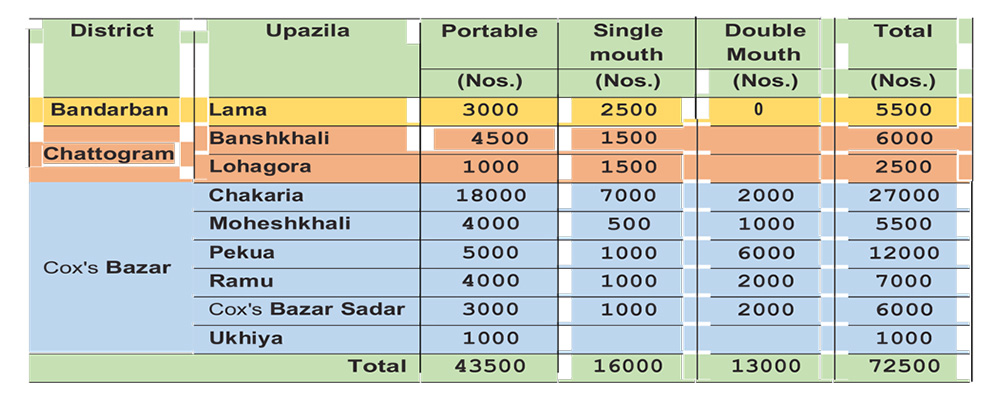
Total 72,500 ICS were installed last year among which 43,500 were Portable, 16,000 Single Burner, and 13,000 Double Burner. District wise and Upazila wise achievements are stated below:
Challenges
• Covid-19 was the greatest challenge last year.
• Lack of adequate financial support to execute the activities at the field level.
• Scarcity of raw material for res production.
• Interruption in supply because of inadequate transportation facilities due to Covid-19 and bad road conditions due to heavy rainfall
• Lack of awareness on the health hazards resulting from smoke and the benefits of using res.
• Financial incapability of the prospective beneficiaries to buy res.
 ICS user at home
ICS user at home
• Yearly reduction of Carbon di oxide emission: 2.145 ton per JCS
• Yearly savings of fuel wood:1.277 ton per stove
• Fuel and time consumption of ICS:
50% less than traditional stove
• Almost Smoke Free environment that ensures healthy life, especially of mother and children.
Lesson Learned
• Involvement of community leaders gives easy access to any community.
• To proliferate the use of res, widespread promotion is needed across the country.
• Staff capacity needs to be developed by training.
• Involvement of community leaders, Local government and general physicians can improve the users’ awareness.
• Local or women entrepreneurship may be developed for reaching out to the beneficiaries in every village for providing res in every village to reach the beneficiary easily.

